STEAM education aims to develop different student capabilities to solve real life problems. With the fast changing world and tremendous amount of information, developing students’ 21st century skills (also known as generic skills) is key to prepare them for unprecedented challenges and the future. Through STEAM education, students build solid knowledge and skills of STEAM related disciplines, develop 21st century skills and acquire the ability “to integrate and apply their knowledge and skills across different subject disciplines through solving daily life problems with practical solutions and innovative designs” (CDC, 2015, p. 2).
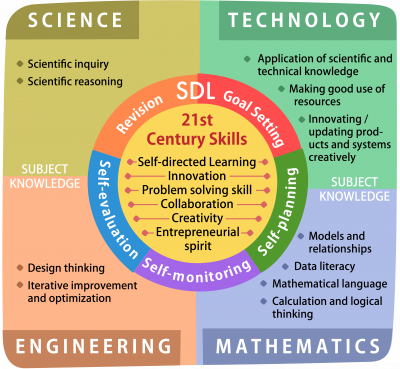
Effective STEAM education enables students to integrate and apply knowledge and skills of different STEAM related disciplines. Integrated STEM education (or sometimes known as interdisciplinary STEM education or integrative STEM education) emphasizes integration and application of two or more STEM related disciplines in solving real life problems (Bryan, et al., 2015; Bybee, 2014; English, 2016; Johnson, 2013; Kelley & Knowles, 2016; Laboy-Rush, 2011; Moore, et al, 2015; Sanders, 2009). According to a study by Tasiopoulou et al.(as cited in Vakkou et al., 2023), integrated STEAM education also refers to the integration of at least two STEAM subjects into the development of learning activity sequences and comprehensive lesson plans that emphasise the exploration of real-world problems. The integration highlights also adoption of different disciplinary practices that students are enabled to experience in STEAM education what scientists, engineers and/or mathematicians tend to consider and do when they undergo investigation or solve problems e.g. a self-directed approach.
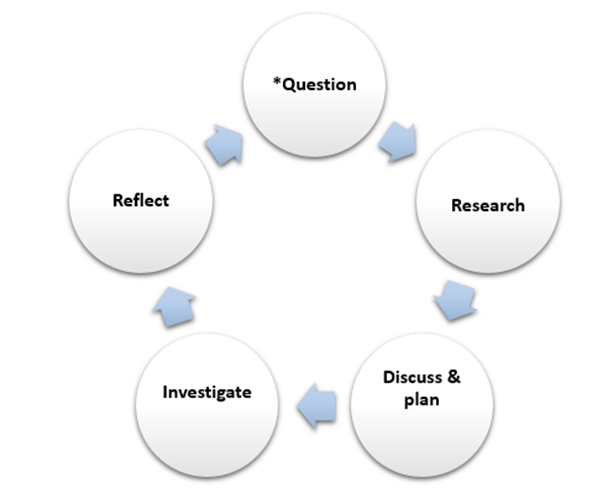
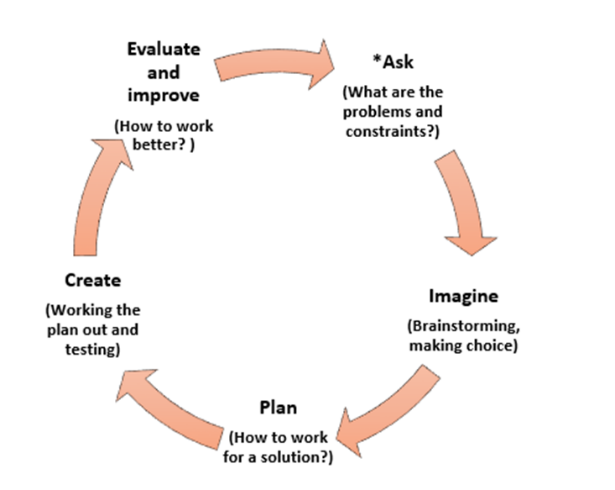
It is not necessary to pursue the integration of all four STEAM disciplines at one time. The emphasis is on raising students’ awareness of the importance of different STEAM related disciplines and knowledge integration. The integration aims to enhance student learning and achieve positive learning outcomes as shown at the center of the conceptual framework for STEAM education (Figure 1).
Reference:
- Bryan, L. A., Moore, T. J., Johnson, C. C., & Roehrig, G. H. (2015).Integrated STEM education. In C. C. Johnson, E. E. Peters-Burton, & T. J. Moore (Eds.), STEM roadmap: A framework forintegration (pp. 23–37). London: Taylor & Francis.
- Bybee, R. W. (2014). NGSS and the next generation of science teachers. Journal of science teacher education, 25(2), 211-221.
- Curriculum Development Council. (2015). Promotion of STEM Education – Unleashing Potential in Innovation. Education Bureau, Hong Kong. https://www.edb.gov.hk/attachment/en/curriculum-development/renewal/Brief%20on%20STEM%20(Overview)_eng_20151105.pdf
- English, L. D. (2016). STEM education K-12: Perspectives on integration. International Journal of STEM education, 3, 1-8.
- Johnson, C. C. (2013). Conceptualizing Integrated STEM Education. School Science and Mathematics, 113(8), 367–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/ssm.12043
- Kelley, T. R., & Knowles, J. G. (2016). A conceptual framework for integrated STEM education. International Journal of STEM education, 3, 1-11.
- Laboy-Rush, D. (2011). Integrated STEM education through problem-based learning. [White paper]. Retrieved from http://www.slideshare.net/dlaboyrush/integrating-stem-educationthrough-project-based-learning
- Moore, T. J., Johnson, C. C., Peters-Burton, E. E., & Guzey, S. S. (2015). The need for a STEM road map. STEM road map: A framework for integrated STEM education, 1.
- Sanders, M. (2009, December). STEM, STEM education, STEMmania. The Technology Teacher, 68(4), 20-26.
- Vakkou, K. Α., Hovardas, T., Xenofontos, N., & Zacharia, Z. C. (2023). Comparing Expert and Peer Assessment of Pedagogical Design in Integrated STEAM Education. In The Power of Peer Learning: Fostering Students’ Learning Processes and Outcomes (pp. 121-141). Cham: Springer International Publishing.

